Analyzing data patterns and different classification methods
The objective of this assignment was to install scikit-learn library for python, retrieve
language dataset from DSL and perform language classification using four different machine
learning algorithm. After training the models, we ran accuracy test for all the models in the
pipeline to showcase which model had the highest accuracy.
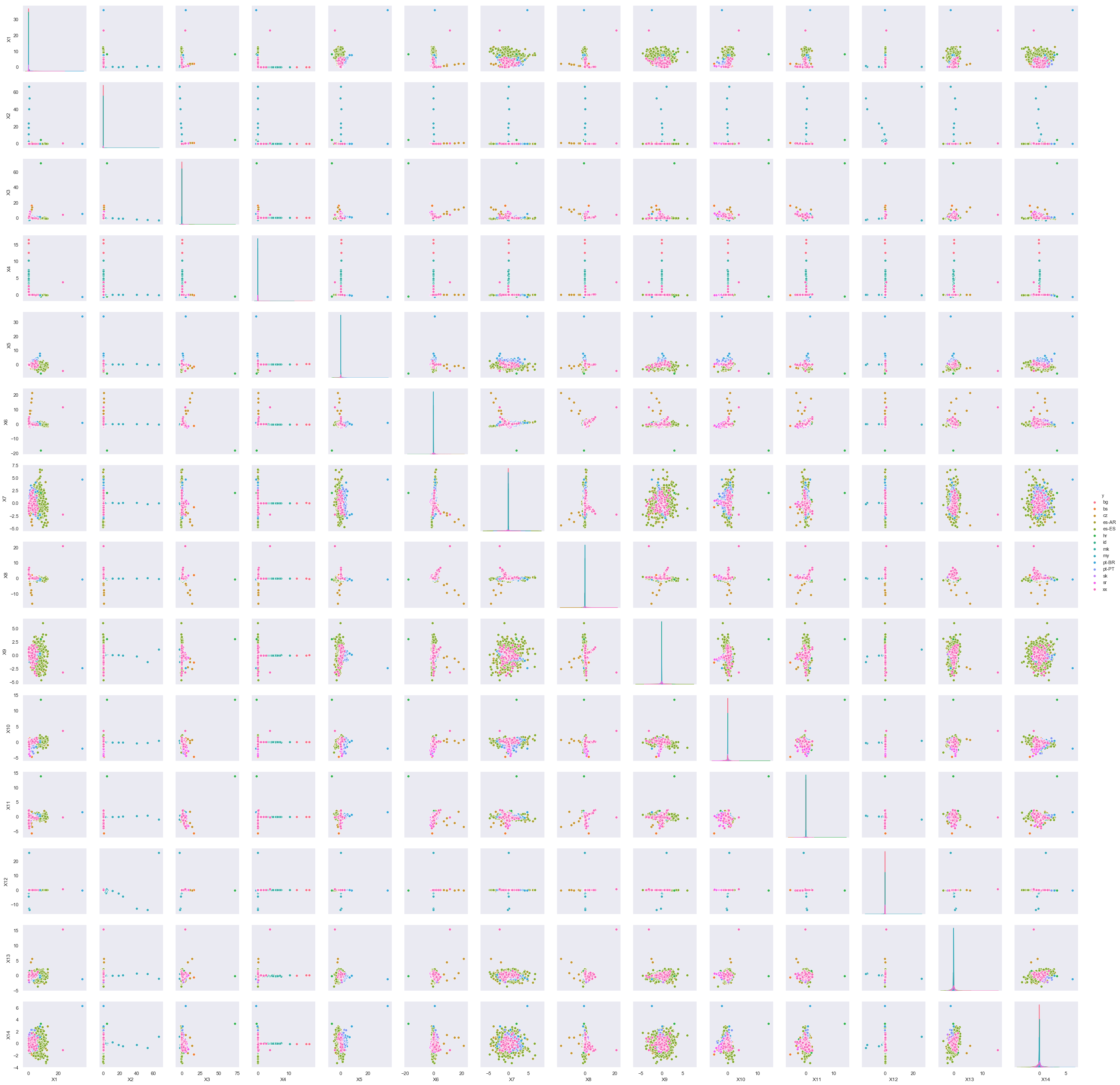
Before extracting the features from the training dataset, we ran PCA to determine which
labels are best fit for classification by performing Kbest method using chi-square. The data
was dense and it doesn’t really work properly with PCA, so we used truncatedSVD to plot
the relation in figure[1]. The plots helps us to understand the label subsequently saving us
the time to train the data by eliciting the relation between each feature with other. The plot
also helps us to visualize the number of labels present in the data viz. 14.
We were instructed to use four different classification algorithms namely, Naive Bayes,
LinearSVC, Decision Tree and Logistic Regression. We loaded all the models in a pipeline
and we store it in a python dictionary to loop over them one after the other.
Naive Bayes
We used multinomial NB (Naive Bayes)[3] to perform ‘transform’ on our data and we used
countvectorizer, feature selection and the model itself in our pipeline.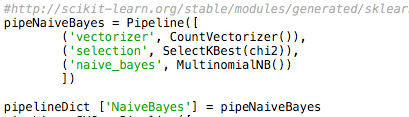
Code to save NB in pipeline [Figure 2]
Naive Bayes uses a prior data (known knowledge) to classify the data into different labels.
Since the data had more than two labels we went with Multinomial NB algorithm to perform
classification.
Logistic Regression
Logistic regression[4] is well known algorithm in classification. We played around with this
algorithm and figured that ‘newton-cg’ was solver for this particular dataset. Since, the
sigmoid and tanH functions were not giving us the accuracy we were expecting, we used
‘newton-cg’.
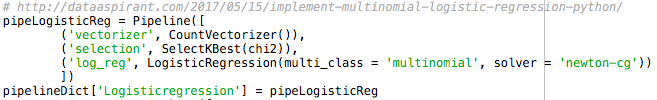
Code to save Logistic Regression in pipeline [Figure 3]
Decision Tree Classifier
Usually Decision Tree[1] is used for predictive analysis, but it also has the capability to
perform classification. It one of widely used algorithm used in Machine Learning. It is the
foundation that runs the random forest classifier.
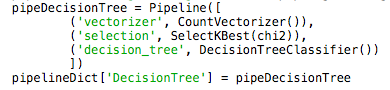
Code to save Decision tree in pipeline [Figure 4]
LinearSVC
LinearSVC[2] uses the One-vs-All (also known as One-vs-Rest) multiclass reduction. It is
also noted here. Also, for multi-class classification problem SVC fits K * (K - 1) / 2 models
where K is the amount of classes.

Code to save LinearSVC in pipeline [Figure 5]

The Confusion Matrix of LinearSVC
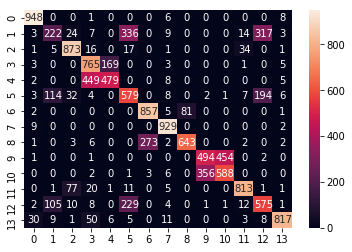
Confusion Matrix of LinearSVC [Figure 6]
The confusion Matrix for Decision Tree
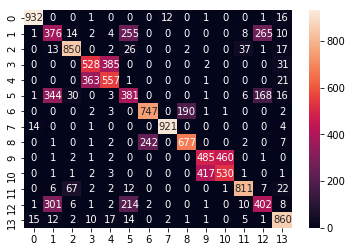
Confusion Matrix of Decision Tree [Figure 7]
The confusion Matrix for Naive Bayes
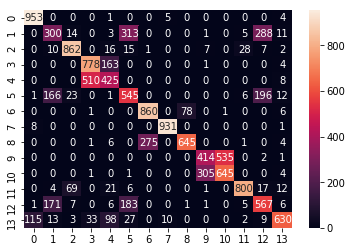
Confusion Matrix of Naive Bayes [Figure 8]
The confusion Matrix for Logistic Regression
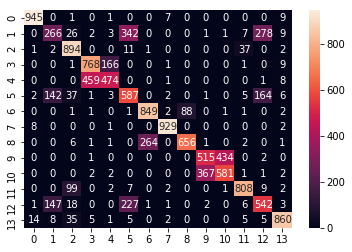
Confusion Matrix of Logistic Regression [Figure 9]
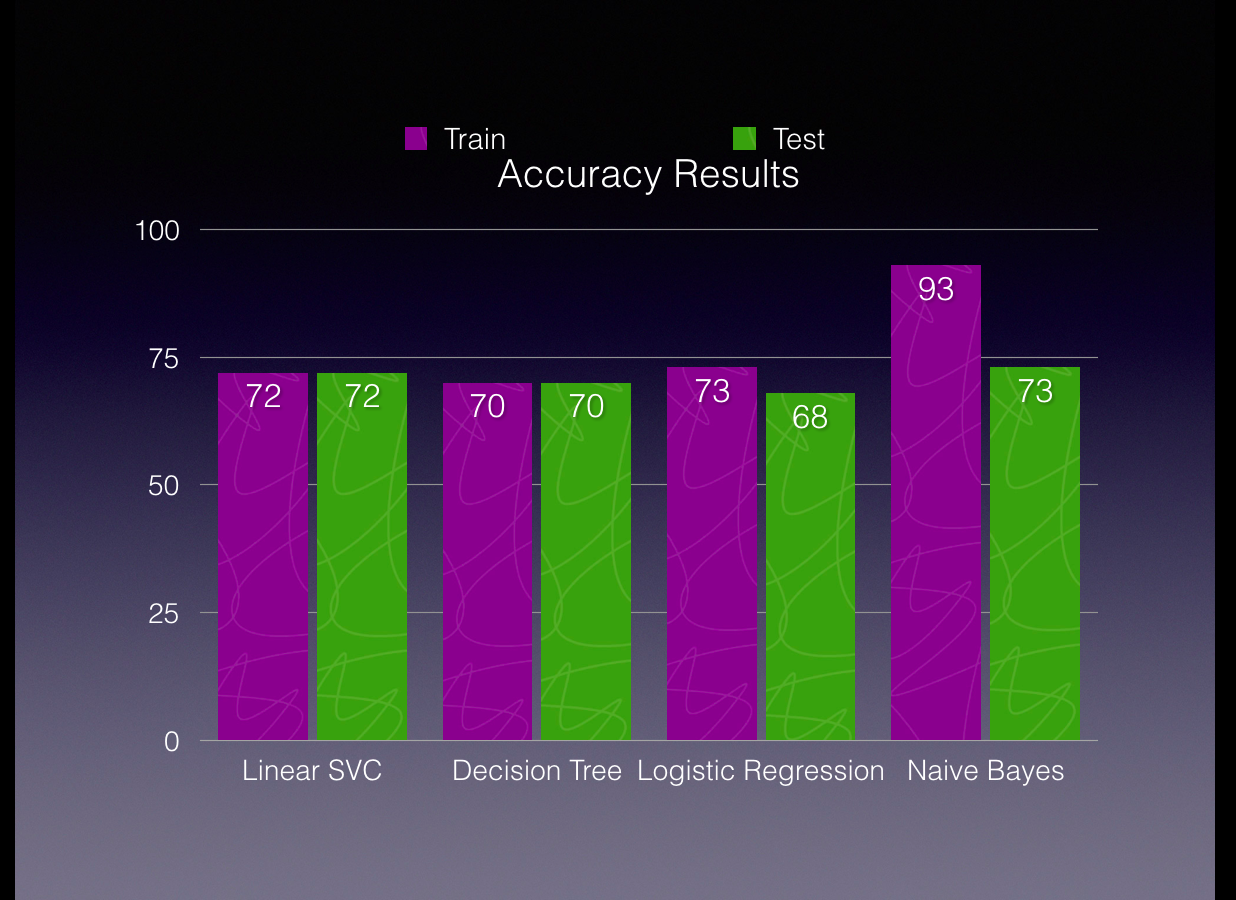
Accuracy of all models Train V Test [Figure 10]
We can clearly see that the accuracy of Naive Bayes was higher during the training
however the model didn’t perform that well when it saw unseen data. LinearSVC, on
the other hand, performed consistently across train and test data.
[1] scikit-learn, “scikit-learn,” [Online]. Available:
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier.html#skle
arn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier. [Accessed 29 07 2018].
[2] “svc,” [Online]. Available:
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.svm.LinearSVC.html. [Accessed 29
07 2018].
[3] “naivebayes,” [Online]. Available:
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.naive_bayes.MultinomialNB.html.
[Accessed 29 07 2018].
[4] “logreg,” [Online]. Available:
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression.htm
l. [Accessed 29 07 18].